
Established in 2004, CIDP (Centre International de Développement Pharmaceutique) is an international Contract Research Organisation (CRO) that carries out high R&D activities for pharmaceutical, medical device, nutraceutical and cosmetic industries.
Anti-pollution

ANTI POLLUTION STUDIES
Air pollution consisting of particulate matter (PM 2.5, PM 10), Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH), Volatile organic Compounds (VOC) and Ozone among others is considered as the second most important cause of extrinsic cutaneous ageing, cutaneous oxidative stress and formation of pigmentary spots. Standardized efficacy tests have therefore become necessary.
To evaluate the efficacy of cosmetic product to protect against the detrimental effect of pollution, CIDP has developed two methodologies:
- An indoor controlled Pollution Exposure System (CPES) :
A novel method for evaluating the effect of pollution on the human skin under controlled conditions Curpen et al., 2020
- An outdoor system (real polluted conditions)
An indoor controlled Pollution Exposure System (CPES)
CIDP has developed a Controlled Pollution Exposure System (CPES) which allows the in vivo (on human volunteers), in vitro (on monolayer cell culture) and ex vivo (on human skin explants or natural hair strands) controlled exposure to pollutants. Numerous pollutants can be evaluated using the CPES including Ozone, Particulate Matter, Ambient Dust, Indoor dust, Diesel...
This unique system allows on-line monitoring and control of the concentration and flux of different pollutants to which the skin is exposed to. The system also allows to evaluate the combined effect of pollutants with light such as UV, blue light…
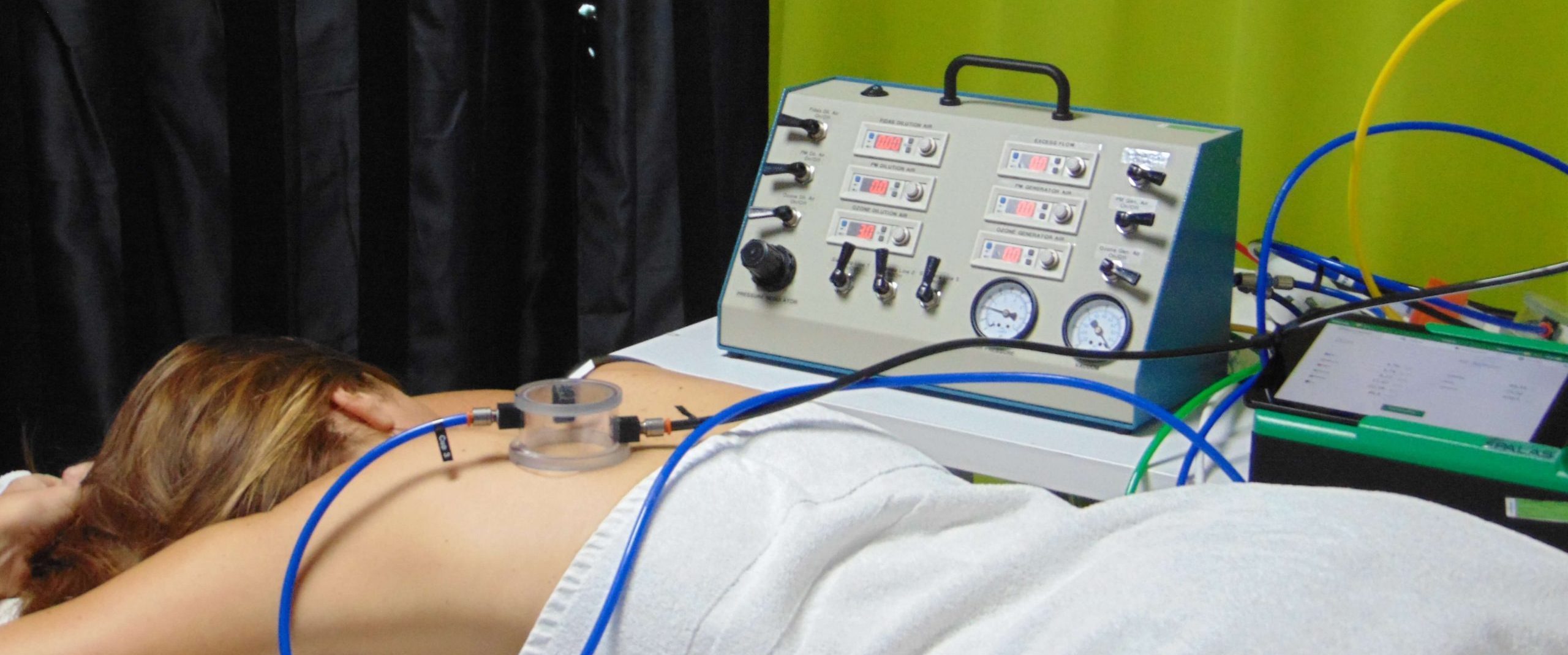
METHODOLOGY
Different methodologies have been developed in house and allows the evaluation of the protective antioxidant, barrier, and cleansing efficacy of anti-pollution products.
Different markers can be analysed including:
- Oxidative stress biomarkers such as Squalene/Squalene monohydroperoxide, Malondialdehyde (MDA), catalase, protein carbonylation…
- Biophysical biomarkers such as skin elasticity, hydration, skin barrier integrity
- Quantification of pollutants by ICP-MS
- Visualisation of particles by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)


IN VITRO MODEL
Using in vitro (monolayer cell culture) or ex vivo (human skin explants) models,different markers and biochemical pathways can be analysed including:
- Oxidative stress biomarkers such as Reactive Oxygen species (by the DCFH-DA method), Squalene/Squalene monohydroperoxide, Malondialdehyde (MDA), catalase, NRF-2 activity
- Ageing markers such as MMP-1, collagen bundles (by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)), pro-collagen, collagen immunostaining
Pro-inflammatory cytokines induction such as IL-1α, IL-6 etc.
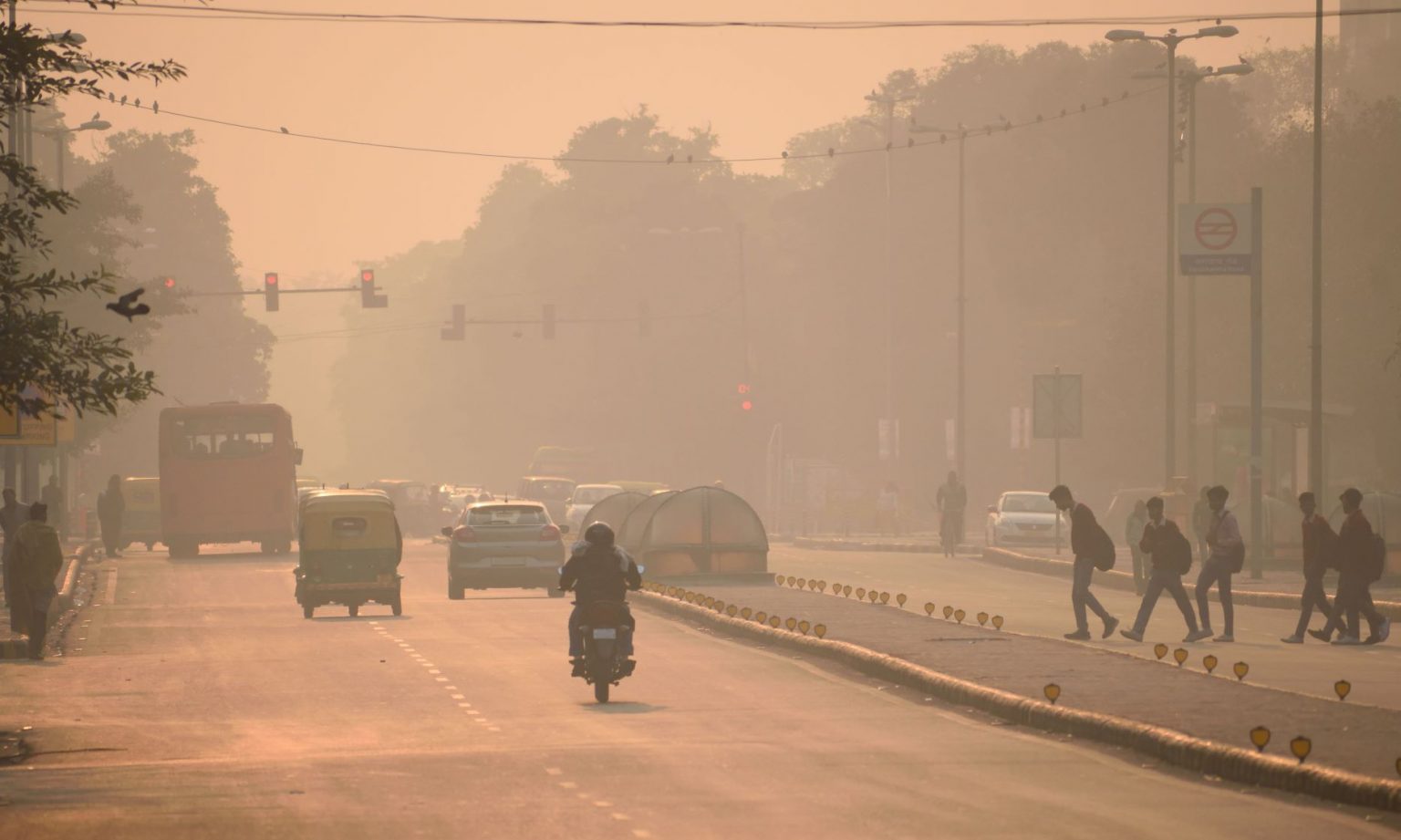
An outdoor system (real polluted conditions)
The detrimental impact of air pollutants can also be evaluated by performing the study in highly polluted regions such as New Delhi.
CIDP has also designed protocols to monitor the efficacy of anti-pollution products in real polluted conditions. The study can be conducted in CIDP India which is localised in the highly polluted centre of New Delhi.

BIOMARKERS ANALYSED
- Oxidative stress biomarkers such as Squalene/Squalene monohydroperoxide, Malondialdehyde (MDA), protein carbonylation…
- Biophysical biomarkers such as skin elasticity, hydration, skin barrier integrity
- Quantification of pollutants by ICP-MS
- Visualisation of particles by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)